Eyes in the Sky: How Drones Are Transforming Insurance Claims

Insurance companies are taking to the skies – literally. In 2026, drone pilots are in high demand, revolutionizing the way claims are processed across the United States. From assessing storm damage in the Midwest to inspecting high-rise buildings in New York City, drones are proving to be invaluable tools for insurers.
This shift isn’t just about flashy technology; it’s about efficiency, accuracy, and ultimately, better service for policyholders. Let’s explore why insurance companies are increasingly relying on drone pilots and how this trend is reshaping the industry.
The Storm Chaser’s New Tool: Faster, Safer Assessments
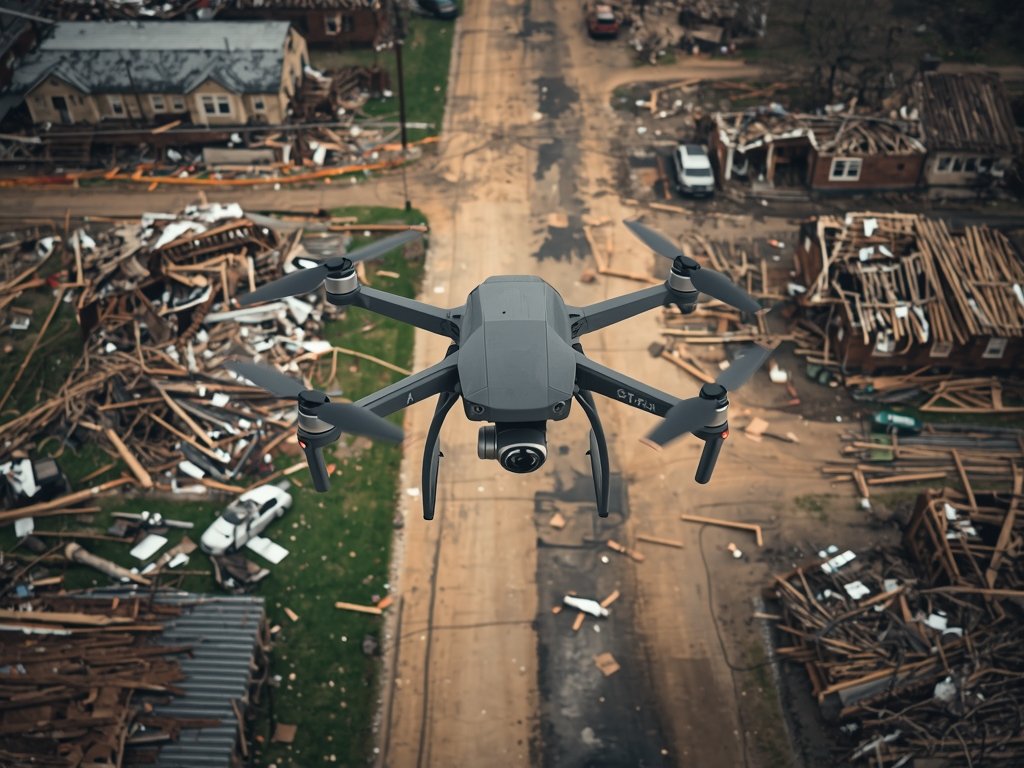

Remember the devastating tornadoes that ripped through Oklahoma last year? In the aftermath, insurance adjusters faced a daunting task: assessing widespread damage across vast areas. Traditionally, this meant boots on the ground, climbing ladders, and navigating hazardous conditions.
Drone Advantages in Disaster Zones
Enter drones. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal imaging, these aerial vehicles can quickly survey damaged properties, providing detailed images and data to adjusters. This not only speeds up the claims process but also keeps adjusters out of harm’s way.
Imagine a drone hovering over a collapsed roof, capturing every detail of the damage. This data can be instantly transmitted to an adjuster, allowing them to make informed decisions without setting foot on the precarious structure.
Real-World Impact: Hurricane Ian’s Aftermath
The benefits of drone technology were evident in the wake of Hurricane Ian, which ravaged Florida in 2022. Insurance companies deployed drones to assess damage across the state, significantly reducing the time it took to process claims and get much-needed funds to policyholders.
Beyond Disasters: Everyday Applications of Drone Technology

While drones are invaluable in disaster zones, their applications extend far beyond catastrophic events. Insurance companies are increasingly using drones for routine inspections, risk assessments, and even fraud detection.
Routine Inspections Made Easy
Consider a large commercial property with a sprawling roof. Traditionally, inspecting such a roof would require a team of workers, scaffolding, and potentially days of work. A drone can complete the same inspection in a fraction of the time, providing detailed images and identifying potential issues like leaks or structural damage.
Proactive Risk Management
Drones are also being used for proactive risk management. By regularly inspecting properties, insurers can identify potential hazards before they become major problems. For example, a drone might spot a weakened tree branch that could fall on a house during a storm, allowing the insurer to recommend preventative measures to the policyholder.
The Human Factor: Drone Pilots in Demand

The rise of drone technology has created a new and exciting career path: drone pilot. Insurance companies are actively recruiting pilots with the skills and certifications needed to operate these sophisticated machines.
Skills and Qualifications
Becoming a drone pilot for an insurance company requires more than just flying skills. Pilots need to be proficient in data analysis, have a strong understanding of insurance principles, and possess excellent communication skills. They must also be able to work independently and make sound judgments in often challenging situations.
A Growing Industry
The demand for qualified drone pilots is expected to continue growing in the coming years. As more insurance companies adopt drone technology, the need for skilled operators will only increase. This presents a unique opportunity for individuals looking for a rewarding career in a rapidly evolving field.
Regulatory Landscape: Navigating the Skies
Operating drones for commercial purposes is not without its challenges. The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has strict regulations governing drone flights, including restrictions on altitude, proximity to airports, and flight times.
Part 107 Certification
To fly drones commercially, pilots must obtain a Part 107 certification from the FAA. This involves passing a knowledge test and meeting specific flight experience requirements. Insurance companies ensure their pilots are properly certified and adhere to all FAA regulations.
Evolving Regulations
As drone technology advances, so too do the regulations surrounding their use. Insurance companies must stay abreast of these changes to ensure compliance and maintain safe operations. This includes keeping up with updates to airspace restrictions, privacy laws, and data security protocols.
The Future of Insurance: A Bird’s-Eye View

The integration of drone technology into the insurance industry is still in its early stages, but the potential is vast. As drones become more sophisticated and regulations evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications in the years to come.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Drone technology has the potential to significantly enhance the customer experience. Faster claims processing, more accurate assessments, and proactive risk management all contribute to a more efficient and responsive insurance system. Policyholders can expect quicker payouts and a more personalized approach to their coverage.
Data-Driven Insights
The data collected by drones can provide valuable insights into risk patterns and trends. By analyzing this data, insurance companies can develop more accurate pricing models, identify emerging risks, and offer tailored coverage options to their customers.
FAQ
How much do drone pilots earn in the insurance industry?
Salaries for drone pilots in the insurance industry vary depending on experience, location, and the specific company. However, the average salary typically ranges from $60,000 to $90,000 per year.
What kind of drones are used for insurance inspections?
Insurance companies typically use high-quality drones equipped with advanced cameras, thermal imaging sensors, and GPS technology. Popular models include the DJI Matrice and Phantom series.
Are there any privacy concerns with using drones for insurance inspections?
Yes, privacy is a major concern. Insurance companies must adhere to strict guidelines to protect the privacy of individuals and property owners. This includes obtaining necessary permissions and avoiding capturing unnecessary data.
How long does it take to become a certified drone pilot?
The time it takes to become a certified drone pilot varies depending on individual learning pace and prior experience. However, most people can obtain their Part 107 certification within a few months of dedicated study and practice.
What are the career prospects for drone pilots in the insurance industry?
The career prospects for drone pilots in the insurance industry are excellent. With the growing adoption of drone technology, demand for qualified pilots is expected to remain high, offering opportunities for advancement and specialization.
Your definitive resource for drone technology. From expert reviews of the latest DJI models to professional Part 107 flight training and industry regulations




